Medieval arrows caused injuries similar to modern gunshot wounds, according to archaeologists analysing newly-discovered human remains.
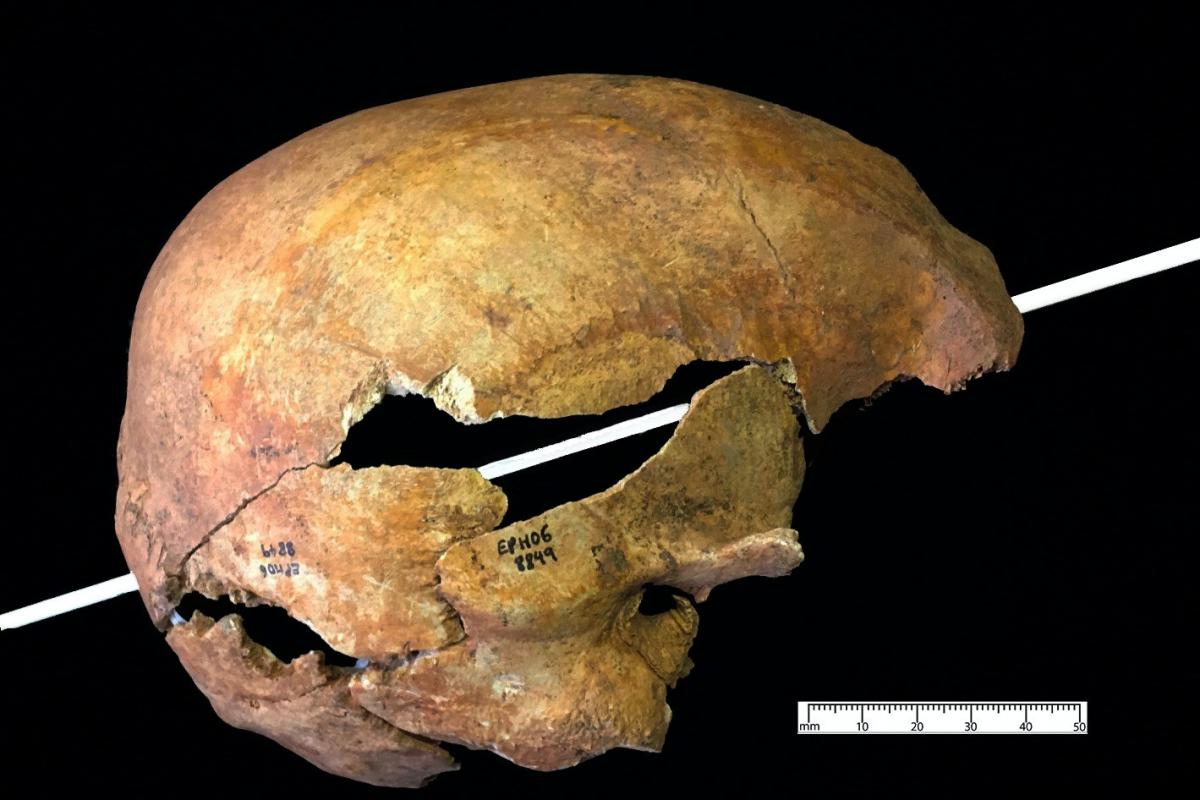
The bones, recovered from a Dominican friary in Exeter, show arrows fired from longbows could penetrate right through the human skull, creating small entry and large exit wounds.
The human skeletons examined as part of the study, who had possibly died in battle, had been moved from an original burial location elsewhere to this consecrated holy ground later.

The English longbow was renowned for its potency and archers played a critical role in famous English military victories, including the battles of Agincourt and Crecy.
The depiction of King Harold with an arrow in his eye in the Bayeux Tapestry is one of the most iconic images of English history but actual traces of the physical effects of arrows on humans are exceptionally rare.
The research, by a team based at the University of Exeter, shows medieval arrows may have been designed to spin clockwise as they hit the victim.
Archaeologist Professor Oliver Creighton, who led the research, said: “These results have profound implications for our understanding of the power of the medieval longbow; for how we recognise arrow trauma in the archaeological record; and for where battle casualties were buried.
“In the medieval world, death caused by an arrow in the eye or the face could have special significance.
“Clerical writers sometimes saw the injury as a divinely ordained punishment, with the ‘arrow in the eye’ which may or may not have been sustained by King Harold II on the battlefield of Hastings in 1066 the most famous case in point.
“Our study brings into focus the horrific reality of such an injury.”
The burial ground at the Dominican Friary was excavated by Exeter Archaeology between 1997 and 2007 in advance of the construction of the Princesshay shopping precinct in Exeter city centre.
In the burial ground was a collection of disarticulated remains, including 22 bone fragments and three teeth.
All these bones showed evidence of traumatic injuries caused by fractures that occurred at or around the time of death, most likely caused by arrow trauma.
These injuries included a puncture wound to the cranium on the top of the right eye and an exit wound at the back of the head.

In this case, the arrow was probably spinning clockwise when it hit the man’s head.
Another puncture wound was found in a right tibia, near to where the top of the calf would have been.
The arrow had passed through the flesh of the lower leg from behind before being lodged in the bone.
It is thought the arrowhead was an armour-piercing type known as a “bodkin” type, square or diamond shaped in section, suggesting among the remains is someone killed in battle, or by someone with military-style equipment.
It is likely that while the arrowhead exited the skull the arrow shaft remained lodged and was later retracted back through the front of the head, creating more fractures to the bone.
It is well known that medieval arrows were fletched to enable arrows to spin in order to maximise their stability in flight and accuracy, but the puncture wound provides evidence this arrow at least was fletched to spin clockwise as it hit a victim.
Gun manufacturers have predominantly rifled barrels so that bullets spin in the same, clockwise, direction.



Comments: Our rules
We want our comments to be a lively and valuable part of our community - a place where readers can debate and engage with the most important local issues. The ability to comment on our stories is a privilege, not a right, however, and that privilege may be withdrawn if it is abused or misused.
Please report any comments that break our rules.
Read the rules here